New updated Lead4Pass 300-410 Dumps with PDF file and VCE practice exam engine to help pass the 300-410 ENARSI Exam successfully!
Lead4Pass 300-410 exam dumps contain 608 exam questions and answers, covering complete CCNP Enterprise 300-410 ENARSI certification exam questions, and verified to be true and valid, check here to get the latest Lead4Pass 300-410 dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (Include 2022 Newest Simulation Labs).
And, download a partial Lead4Pass 300-410 dumps from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Q5zIxqFRkF6FTyIj-xj2Q0nWn4J5Eg_X/
Also, read the latest 15 Lead4Pass 300-410 dumps exam questions and answers online:
| Number of exam questions | Exam name | From | Release time | Previous issue |
| 10 | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) | Lead4Pass | Nov 21, 2022 | [Updated Oct 2022] 300-410 dumps questions |
New Question 1:
You manage the EIGRP subnet in your organization. You have enabled EIGRP for IPv6 on all the routers in the EIGRP AS 355 using the following commands on all the routers: The ipv6 unicast-routing command in global configuration mode The interface command in global configuration mode The ipv6 enable command in interface configuration mode The ipv6 eigrp command in interface configuration mode The ipv6 router eigrp command in global configuration mode The eigrp router-id command in global configuration mode
During verification, you discover that EIGRP for IPv6 is not running on the routers. Which of the following should be done to fix the issue?
A. The ipv6 address command should be executed in interface configuration mode.
B. The ipv6 address command should be executed in router configuration mode.
C. The eigrp router-id command should be executed in interface configuration mode.
D. The eigrp router-id command should be executed in router configuration mode.
Correct Answer: D
The eigrp router-id command should be executed in router configuration mode to fix the issue. This command specifies a fixed router IPv4 address to the router. If this command is missing or incorrectly configured on the router, EIGRP for IPv6 will not run properly.
Another command that you should perform so that EIGRP for IPv6 runs on the routers is the no shutdown command. You should execute this command in interface configuration mode. The no shutdown command is necessary because all the interfaces with EIGRP for IPv6 enabled on them are in a shutdown state by default.
A sample configuration to implement EIGRP for IPv6 on a router is as follows:
rtrA(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
rtrA(config) # interface Fa0/1
rtrA(config-if) # ipv6 enable
rtrA(config-if) # ipv6 eigrp 355
rtrA(config-if)# no shutdown
rtrA(config-if) # exit
rtrA(config)# ipv6 router eigrp 355
rtrA(config-rtr)# eigrp router-id 1.1.1.1
The two options stating that the ipv6 address command should be executed on the routers are incorrect. EIGRP for IPv6 can be configured on router interfaces without explicitly specifying a global unicast IPv6 address. If you specify the ipv6 enable command, as in this scenario, then the ipv6 address command is not required.
The option stating that the eigrp router-id command should be executed in interface configuration mode is incorrect. This command should be executed in router configuration mode instead of interface or global configuration modes.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Identify IPv6 addressing and subnetting
References:
Cisco IPv6 Implementation Guide, Release 15.2MandT > Implementing EIGRP for IPv6 > How to Implement EIGRP for IPv6 > Enabling EIGRP for IPv6 on an Interface
New Question 2:
What are the two functions of IPv6 Source Guard? (Choose two.)
A. It works independently from IPv6 neighbor discovery.
B. It denies traffic from unknown sources or unallocated addresses.
C. It uses the populated binding table for allowing legitimate traffic.
D. It denies traffic by inspecting neighbor discovery packets for specific patterns.
E. It blocks certain traffic by inspecting DHCP packets for specific sources.
Correct Answer: BC
IPv6 source guard is an interface feature between the populated binding table and data traffic filtering. IPv6 source guard can deny traffic from unknown sources or unallocated addresses.
New Question 3:
Refer to the exhibit.
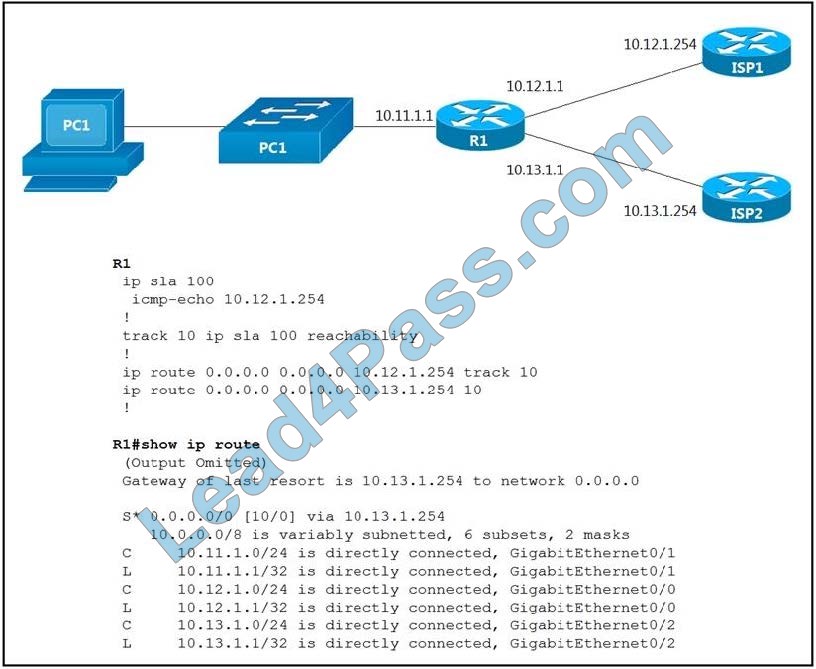
An engineer is monitoring the reachability of the configured default routes to ISP1 and ISP2. The default route from ISP1 is preferred if available. How is this issue resolved?
A. Use the ICMP-echo command to track both default routes
B. Use the same AD for both default routes
C. Start IP SLA by matching numbers for track and IP SLA commands
D. Start IP SLA by defining frequency and scheduling it
Correct Answer: D
In the above configuration, we have not activated our IP SLA operation.
We can start it with this command:
R1(config)#ip sla schedule 100 life forever start-time now
Also, we should specify the rate of ICMP echo:
R1(config-IP-SLA-echo)#frequency 5 // Send ICMP echo every 5 seconds
New Question 4:
Refer to the exhibit.
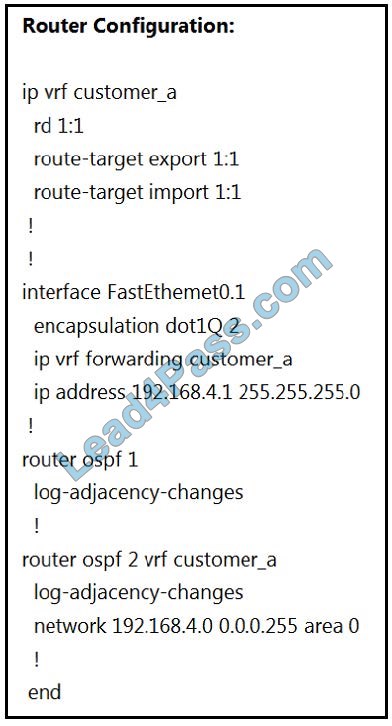
The network administrator configured VRF lite for the customer The technician at the remote site misconfigured VRF on the router. Which configuration will resolve connectivity for both sites of customer a?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: D
From the exhibit, we learned:
+
VRF customer_a was exported with a Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site, it must be imported with the same RT 1:1.
+
VRF customer_a was imported with a Route Target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site, it must be exported with the same RT 1:1.
Therefore at the remote site, we must configure the command “route-target both 1:1” (which is equivalent to two commands “route-target import 1:1” and “route-target export 1:1”.
New Question 5:
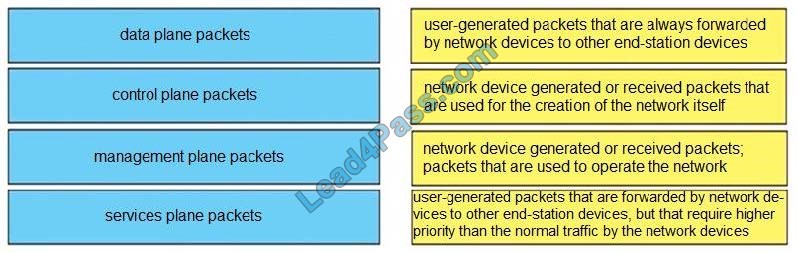
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the packet types from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:
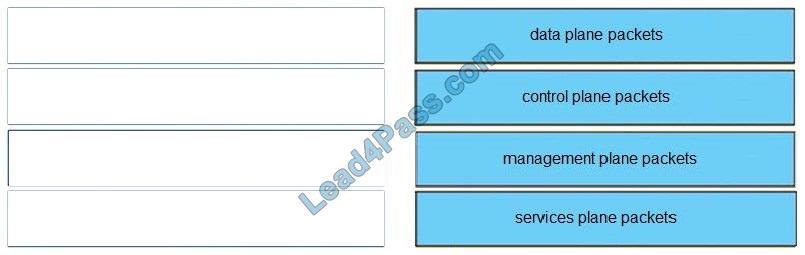
Correct Answer:
Unlike legacy network technologies such as ISDN, Frame Relay, and ATM which defined separate data and control channels, IP carries all packets within a single pipe. Thus, IP network devices such as routers and switches must be able to distinguish between data plane, control plane, and management plane packets to treat each packet appropriately. From an IP traffic plane perspective, packets may be divided into four distinct, logical groups:
1.
Data plane packets -End-station, user-generated packets that are always forwarded by network devices to other end-station devices. From the perspective of the network device, data plane packets always have a transit destination IP address and can be handled by normal, destination IP address-based forwarding processes.
2.
Control plane packets -Network device generated or received packets that are used for the creation and operation of the network itself. From the perspective of the network device, control plane packets always have a receive destination IP address and are handled by the CPU in the network device route processor. Examples include protocols such as ARP, BGP, OSPF, and other protocols that glue the network together.
3.
Management plane packets -Network device generated or received packets, or management station generated or received packets that are used to manage the network. From the perspective of the network device, management plane packets always have a receive destination IP address and are handled by the CPU in the network device route processor. Examples include protocols such as Telnet, Secure Shell (SSH), TFTP, SNMP, FTP, NTP, and other protocols used to manage the device and/or network.
4.
Services plane packets -A special case of data plane packets, services plane packets are also user-generated packets that are also forwarded by network devices to other end-station devices, but that require high-touch handling by the network device (above and beyond normal, destination IP address-based forwarding) to forward the packet.
Examples of high-touch handling include such functions as GRE encapsulation, QoS, MPLS VPNs, SSL/IPsec encryption/decryption, etc. From the perspective of the network device, service plane packets may have a transit destination IP address or may have a receive destination IP address (for example, in the case of a VPN tunnel endpoint).
Reference: https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/resources/copp_best_practices
New Question 6:
Refer to the exhibit. The AP status from Cisco DNA Center Assurance Dashboard shows some physical connectivity issues from the access switch interface G1/0/14.
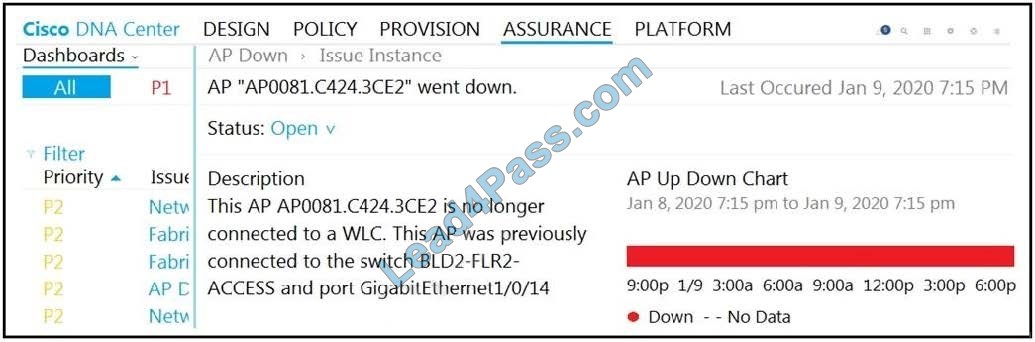
Which command generates the diagnostic data to resolve the physical connectivity issues?
A. check cable-diagnostics TDR interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
B. verify cable-diagnostics TDR interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
C. show cable-diagnostics TDR interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
D. test cable-diagnostics TDR interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
Correct Answer: D
New Question 7:
Which of the following statements is NOT true of NPTv6?
A. is transport agnostic
B. translates the entire IPv6 address to another IPv6 address
C. is checksum neutral
D. translates only the IPv6 prefix
Correct Answer: B
Network Prefix Translation (NPTv6) is a stateless method of translating the prefix of a received IPv6 address to another prefix without changing the host portion of the IPv6 address. Some of its characteristics are:
It supports both means of transport that perform checksums on the IP header and those that do not. It provides a 1-to-1 relationship between the inside and outside prefixes.
It translates only the prefix, and not the entire address.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe IPv6 NAT
References:
Cisco > Publications and Merchandise > The Internet Protocol Journal > Issues > Volume 14, Number 2, June 2011 > IPv6 Site Multihoming Howfunky…a place with useless technical content!>IPv6 to IPv6 Network Prefix Translation or
NPTv6
New Question 8:
Refer to the exhibit. A junior engineer configured SNMP to network devices. Malicious users have uploaded different configurations to the network devices using SNMP and TFTP servers.
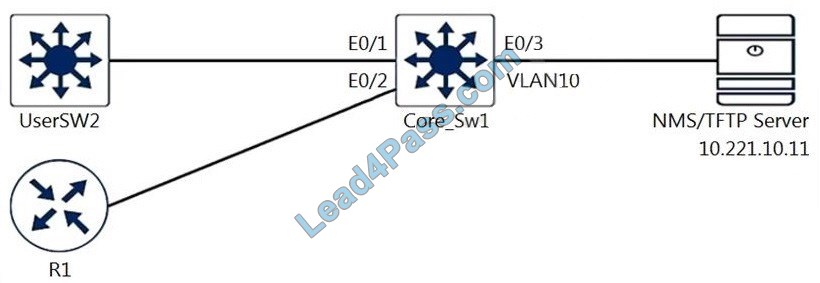
snmp-server group NETVIEW v3 priv read NETVIEW snmp-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NETVIEW write NETADMIN snmp-server community Cisc0Us3r RO snmp-server community Cisc0wrus3r RW
Which configuration prevents changes from unauthorized NMS and TFTP servers?
A. access-list 20 permits 10.221.10.11 access-list 20 to deny any log! SNMP-server group NET VIEW v3 priv read NET VIEW access 20 SNMP-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NET VIEW write NETADMIN access 20 SNMP-server community Cisc0Us3r RO 20 SNMP-server community Cisc0wrus3r RW 20 SNMP-server TFTP-server-list 20
B. access-list 20 permits 10.221.10.11 access-list 20 to deny any log! SNMP-server group NET VIEW v3 priv read NET VIEW access 20 SNMP-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NET VIEW write NETADMIN access 20 SNMP-server community Cisc0wrus3r RO 20 SNMP-server community Cisc0Us3r RW 20 SNMP-server TFTP-server-list 20
C. access-list 20 permits 10.221.10.11 access-list 20 to deny any log
D. access-list 20 permits 10.221.10.11
Correct Answer: A
New Question 9:
Refer to the exhibit. The output of the traceroute from R5 shows a loop in the network. Which configuration prevents this loop?
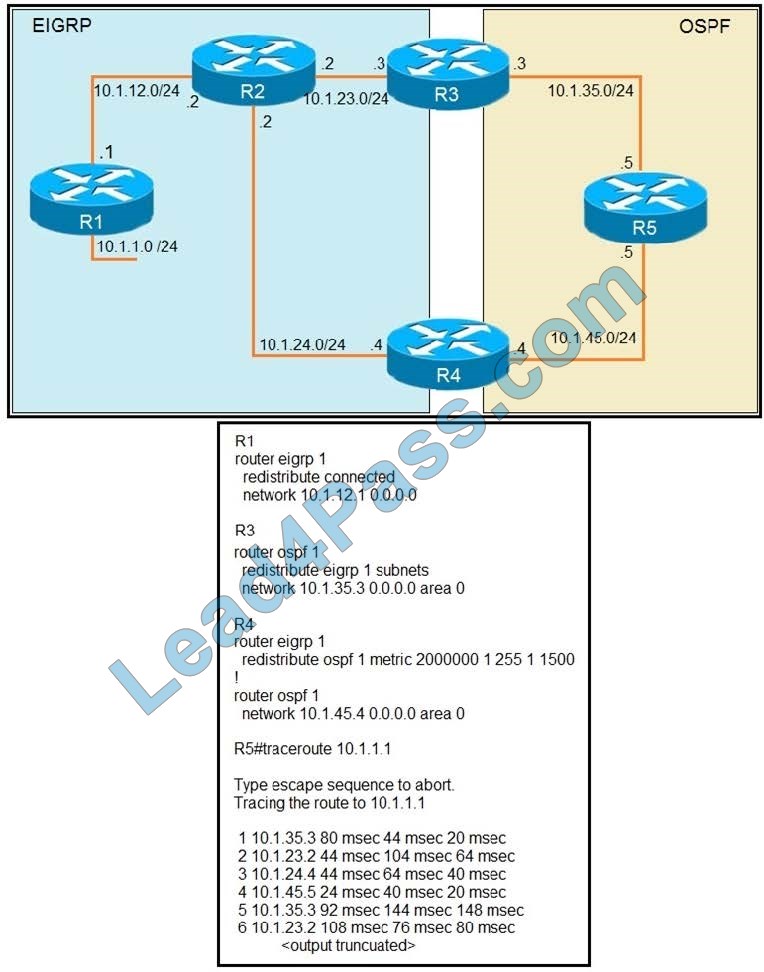

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: A
New Question 10:
Which two methods use IPsec to provide secure connectivity from the branch office to the headquarters office? (Choose two.)
A. DMVPN
B. MPLS VPN
C. Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI)
D. SSL VPN
E. PPPoE
Correct Answer: AC
…
Latest Complete 608 CCNP Enterprise 300-410 Certification Exam Questions With Answers Get Lead4Pass 300-410 Exam Dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (PDF+VCE)
BTW, sharing some more previous free CCNP Enterprise 300-410 PDFs:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1B-r4PbrEKNrBNRiN6uIllaijaHFPkqMk/
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1C3Ny7fnTfs5Vn0f2RRHfve8ZUyogbf9m/
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1GA7Ozk2bKTyvwBiVoCyMSk2jVZ43AD2H/
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Hmd2m8IlFiln0lDicik9brJDd0T1caJr/
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1k425tFP4HR9seCaxmeEkIuaYcXKIU7rk/